In our increasingly fast-paced world, the need for quick and efficient charging has never been greater. Fast chargers have become a staple accessory for many, but there’s often confusion surrounding their wattage ratings. What exactly do those numbers mean, and how do they impact our devices? In this guide, we’ll delve into the world of fast charging to demystify the concept of wattage.
What is Wattage in Fast Charging?
Wattage in fast charging refers to the rate at which electrical power is transferred from the charger to the device being charged. It’s a measure of how quickly a device can be charged.
A watt (W) is a unit of power, and it represents the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit of time. In fast charging, the wattage rating of a charger indicates how much power it can deliver to your device.
The wattage rating on a charger, such as 18W or 30W, indicates the maximum power output it can provide. This wattage rating represents the charger’s capacity to deliver electrical energy to your device.
The higher the wattage, the faster your device’s battery can be charged. This is because a charger with a higher wattage can transfer more power to the device in the same amount of time compared to a charger with lower wattage.
Types of Fast Charging Technologies
Fast charging isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Various technologies have emerged to cater to different devices and ecosystems. Quick Charge, Power Delivery, and proprietary standards from manufacturers all play a role in the fast charging landscape. Importantly, these technologies often come with varying wattage capabilities, which can significantly affect charging times.
Quick Charge
Developed by Qualcomm
Quick Charge is a fast charging technology developed by Qualcomm, a leading semiconductor and telecommunications equipment company.
Widespread Adoption
Quick Charge is commonly found in smartphones, tablets, and other electronic devices. Many Android devices use this technology.
Voltage-Based
Quick Charge primarily relies on increasing the voltage to boost charging speed. It dynamically adjusts the voltage to optimize charging efficiency.
Multiple Versions
Quick Charge has gone through several iterations, with Quick Charge 1.0 to Quick Charge 5.0 being the most prominent. Each version offers improved charging speeds and efficiency.
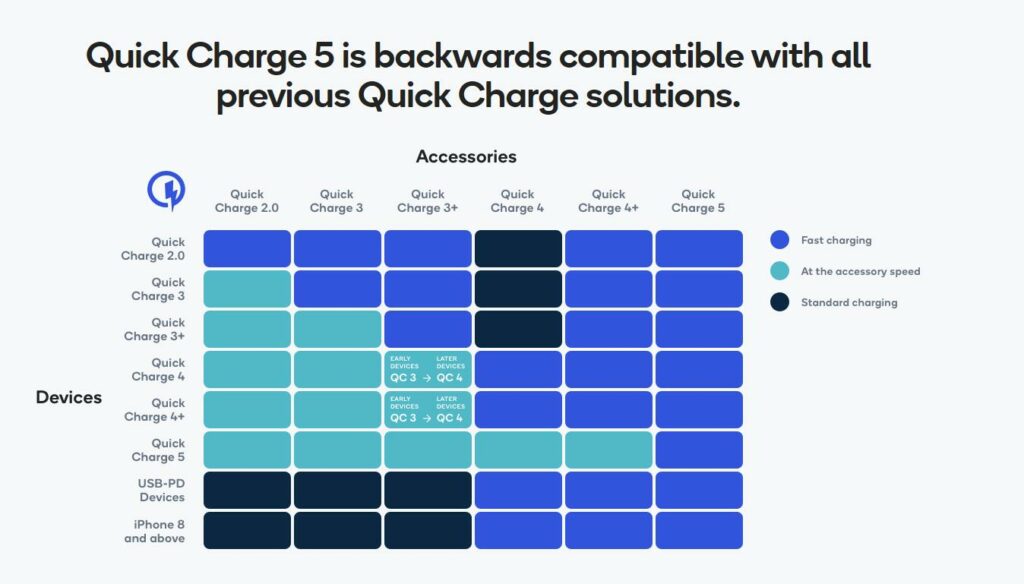
Backward Compatibility
Quick Charge chargers are typically backward compatible with older devices that do not support the latest versions. However, to enjoy the full benefits of Quick Charge, it’s best to pair a compatible charger with a matching device.
Safety Measures
Quick Charge incorporates multiple safety features to protect against overheating, overcharging, and short circuits. These safety mechanisms help ensure a safe charging experience.
Power Delivery (PD)
Developed by USB-IF
Power Delivery is a fast charging protocol developed by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), the organization responsible for USB standards.
Universal Standard
Power Delivery is a universal standard, and it’s not tied to a specific manufacturer. It’s widely adopted in various devices, including smartphones, laptops, tablets, and accessories.
Versatility
One of the significant advantages of Power Delivery is its versatility. It can deliver power at various voltage and current levels, making it suitable for a wide range of devices, from small accessories to large laptops.
Bidirectional Charging
Power Delivery supports bidirectional charging, meaning it can charge both devices (e.g., smartphones) and be used to charge the power source itself (e.g., a laptop).
USB-C Compatibility
Power Delivery often utilizes USB-C connectors, which are reversible and have become a standard for many modern devices. This makes it more convenient for users as they can use a single charger and cable for multiple devices.
Safety and Smart Negotiation
Power Delivery uses a negotiation process between the charger and the device to determine the optimal power delivery, ensuring efficient and safe charging. It also includes safety features to protect against overheating and other potential issues.
Quick Charge VS PD
Development and Compatibility
Quick Charge is developed by Qualcomm and is primarily found in Android devices, while Power Delivery is a universal standard widely adopted across various platforms, including Apple devices and many laptops.
Voltage vs. Versatility
Quick Charge primarily boosts charging speed by increasing voltage, whereas Power Delivery offers versatility by adjusting both voltage and current, making it suitable for a broader range of devices.
Bidirectional Charging
Power Delivery supports bidirectional charging, allowing devices to charge each other or for a device to charge the power source (e.g., a laptop charging a smartphone).
Device Compatibility
When choosing a charger, it’s crucial to match the charger’s wattage with your device’s capabilities. Using a charger with a significantly lower wattage than your device supports will result in slower charging, while using a charger with higher wattage than necessary typically won’t harm your device. However, it’s still wise to stay within the recommended wattage range for optimal performance and safety.
Factors Affecting Charging Speed
Charging speed is influenced by various factors, and understanding these factors can help you optimize the charging process for your devices.
Charger Wattage
The charger’s wattage rating is one of the most critical factors affecting charging speed. A higher-wattage charger can deliver more power to your device, resulting in faster charging. However, it’s essential to use a charger with a wattage that matches your device’s capabilities for optimal performance.
Device Compatibility
The device you’re charging must support the charger’s wattage output. Using a charger with significantly higher wattage than your device can handle won’t necessarily lead to faster charging if your device can’t take advantage of the extra power.
Cable Quality
The quality of the charging cable matters. High-quality, well-insulated cables with good connectors ensure efficient power transfer and minimize power loss, contributing to faster charging.
Device State
The state of your device’s battery can affect charging speed. Charging is typically faster when your device’s battery is low or nearly depleted. As the battery gets closer to a full charge, charging speed may slow down to protect the battery.
Battery Capacity
Devices with larger battery capacities take longer to charge compared to devices with smaller batteries, all else being equal. This is because more energy needs to be transferred to fill a larger battery.
Charging Technology
Different fast charging technologies, such as Quick Charge, Power Delivery, and proprietary standards, can impact charging speed. Your device must support the specific technology used by the charger to take advantage of its fast charging capabilities.
Temperature
Extreme temperatures, whether too hot or too cold, can affect charging speed and battery health. Most devices and chargers have built-in temperature monitoring and safety mechanisms to ensure charging occurs within a safe temperature range.
Background Processes
Running apps and background processes on your device can consume power while charging, potentially slowing down the rate at which the battery charges. Closing unnecessary apps can help maximize charging speed.
Multiple Devices on a Charger
When charging multiple devices simultaneously from a single charger, the total wattage is divided among the devices. This can lead to slower charging for each device compared to charging them individually.
USB Port Type
The type of USB port you’re using can impact charging speed. For instance, USB 2.0 ports generally provide less power compared to USB 3.0 or USB-C ports. Using the appropriate port for your device can optimize charging speed.
Device Settings
Some devices offer settings that allow you to enable or disable fast charging. Ensure that you’ve configured your device to use fast charging when available.
Charger Quality
The quality of the charger itself can affect charging speed. Reputable chargers with advanced electronics and safety features tend to provide more stable and efficient charging.
How to Choose the Right Charger
Check Your Device’s Requirements
Review your device’s manual or specifications to find the recommended charging wattage and voltage. This information is crucial for choosing a compatible charger.
Match the Charger’s Wattage:
Select a charger with a wattage rating that matches or is slightly higher than your device’s recommended wattage. This ensures your device charges at an optimal speed without overloading it.
Consider Charger Compatibility
Ensure that the charger you choose is compatible with your device’s charging port. Most modern devices use USB Type-C, but some may still use Micro USB or Lightning connectors. Select the appropriate cable and charger combination.
Choose a Reputable Brand
Opt for chargers from well-known and reputable brands or manufacturers. These chargers often undergo stringent safety and quality checks, reducing the risk of damage to your device.
Look for Certification
Check if the charger has relevant certifications, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification or USB-IF certification for USB chargers. These certifications indicate compliance with safety and performance standards.
Avoid Cheap Knockoffs:
Avoid purchasing extremely cheap or unbranded chargers from unreliable sources. Low-quality chargers may lack safety features, which can pose risks to your device and personal safety.
Consider Fast Charging Compatibility
If your device supports fast charging, invest in a charger that is compatible with the specific fast charging technology your device uses, whether it’s Quick Charge, Power Delivery, or a proprietary standard.
Multi-Port Chargers
If you have multiple devices to charge, consider multi-port chargers. These chargers allow you to charge multiple devices simultaneously, which can be particularly useful when traveling or in shared spaces.
Cable Quality
Don’t forget to invest in high-quality charging cables. Look for cables with good insulation, sturdy connectors, and the appropriate length for your needs.
Conclusion
In a world where time is of the essence, fast charging has become an invaluable companion for our ever-connected lives. Through this journey into the realm of fast charging, we’ve explored the intricate web of wattage, charging technologies, and the factors that influence our devices’ power replenishment.
Understanding wattage ratings has empowered us to make informed decisions about our chargers, realizing that higher wattage often means faster charging. We’ve grasped the importance of matching charger wattage to our devices, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance.





